From Mindset to Action in Green Export – Part 3: ESG – The Compass for Designing Business Models Toward Green Export

Many businesses tend to think of VSS as a “ticket” and ESG as a “scorecard.” In reality, it should be the other way around: ESG is the operational architecture from within — it determines what you produce, how you produce it, how you manage risk, and how you measure performance. Once that internal system operates stably, VSS becomes merely a verification and standardization step — a shared language with buyers. Rigid trade barriers like MRL or EUDR will continue to exist. Therefore, to go far, businesses must turn market requirements into internal capabilities — namely, data, traceability, and SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures).
From ESG to Business Model Design and Renewal
ESG doesn’t make a business “spend more” — if done right, it helps reduce risks, stabilize operations, and enhance credibility. ESG has a profound impact on three core design blocks: value, cost–productivity, and risk–governance.
It forces us to redefine the value proposition — shifting from “cheap and fast” to “stable, transparent, and safe.” By standardizing processes (e.g., saving water, reducing inorganic inputs, segregating and tracing production flows), quality variability decreases, which in turn lowers risk costs — the often-invisible but expensive burden in export. At the same time, ESG builds a “data discipline” that enables businesses to manage technical barriers (for instance, when the default MRL is 0.01 mg/kg if a substance has no specific limit in the EU) and policy risks (as the EUDR requires geolocation of production areas and segregation between compliant and non-traceable goods).
Two Case Studies – From Field to Model
Let’s look at two real-world examples introduced by Dân Việt newspaper to understand how farmers are moving toward sustainable, green production. In practice, ESG is not a PR slogan; it is a set of technical and management decisions — covering soil, water, fertilizer, labor, and data — that lead to stable productivity, lower risk costs, and “audit readiness.”
Case 1 – A Ngum (Bahnar, Gia Lai):
Since 2022, he has eliminated synthetic chemicals, switched to organic–microbial farming, practiced intercropping, and focused on soil ecosystem health. Results: reduced pests, stable yields, over 3.5 tons of coffee beans per hectare, and nearly VND 300 million net income per year. His farm has become a community learning site, showing clear social (S) impact. In terms of the business model, he repositioned his value from “chemical-intensive, yield-driven” to “safe, consistent, ecosystem-based.” With minimal record-keeping and traceability, his natural model aligns well with VSS frameworks that emphasize soil health and farmer welfare.
Case 2 – Nguyễn An Sơn (Đắk Lắk):
Since 2020, he has adopted multi-stem pruning and drip irrigation with a weekly “nutrition menu”, achieving about 40% water savings, 15–30% less inorganic fertilizer, and five-sixths labor savings. Yields reached ≈5.5 tons/ha (about 1.5 times traditional yields), producing 130 tons in 5 years, worth about VND 8.5 billion, with nearly VND 1 billion in annual profit — along with an OCOP 3-star brand. This is ESG through precision farming: saving resources (E), ensuring labor safety (S), and enforcing procedural and data discipline (G). As a result, meeting VSS and technical requirements becomes much easier.
From Practical Cases to the VSS Roadmap
There are no “shortcuts” to VSS compliance. There are two sustainable paths:
- (i) ESG-first – transform technical and management practices to generate standardized data, or
- (ii) Micro-lot-first – start small but compliant to learn fast and minimize “tuition costs.”
Both converge on data–traceability–SOPs.
When ESG practices become routine processes, requirements like MRL, microbial limits, or EUDR become ordinary management indicators. At that point, VSS serves as a “seal of approval” verifying that the system runs effectively — not a “lifebuoy” in crisis.
Certification investment also becomes easier to budget, as actual costs depend on context and scale, including preparation, evaluation, and maintenance — not just the “audit fee.”
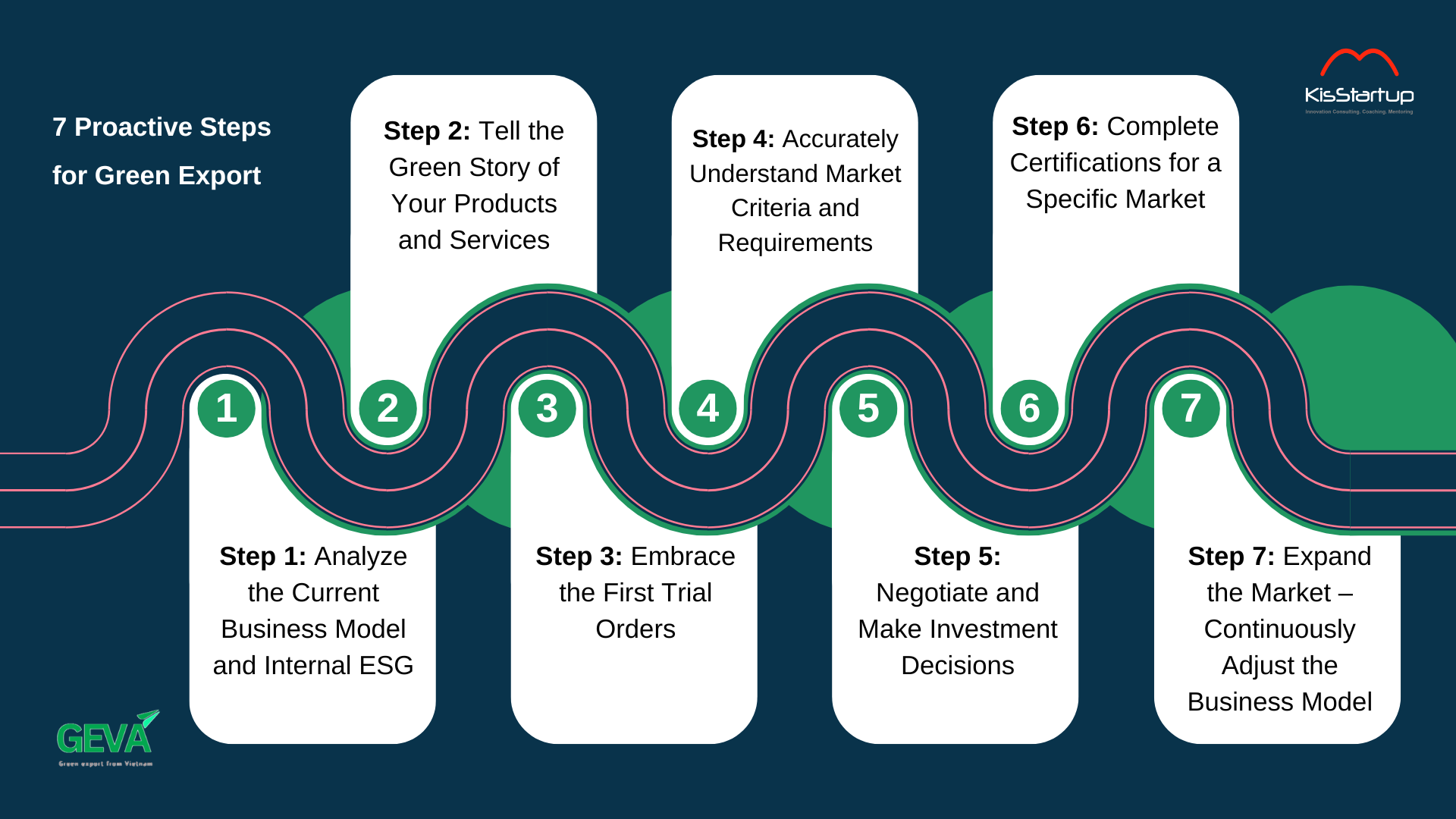
Seven Suggested Steps
- Step 1 – Choose “high-impact, low-cost ESG levers”: irrigation, fertilizer, post-harvest hygiene, and labor safety. Identify 2–3 measurable indicators (moisture, fertilizer dosage, PPE work hours).
- Step 2 – Standardize a small pilot process (micro-lot 5–10%): set short SOPs, assign batch codes, separate storage; do it right, fully, and consistently for one crop season.
- Step 3 – Keep disciplined minimal records: digital or paper farming logs, store input receipts, score compliance weekly.
- Step 4 – Measure core technical indicators: test 1–2 lots for MRL, microbiology, heavy metals; refine processes accordingly.
- Step 5 – Make value transparent: use QR/batch codes linked to field photos, geolocation, simplified SOPs; tell the story of “saving water/reducing fertilizer/ensuring food safety.”
- Step 6 – Cross-check with VSS and test negotiation: compare micro-lot results with 15–25 minimum criteria of a target standard; test-tiered pricing with buyers (small contracts, seasonal improvement clauses).
- Step 7 – Tell your story: share authentic, transparent experiences to build a community of practice. Consolidated data will provide a full picture when proof is needed.
These seven steps effectively “package ESG” into business modules — each creating a data asset and a new operational capability — the very elements VSS measures and customers pay for when you can prove them.
Avoid Two Common “Traps” in VSS Implementation
In reality, costs often “inflate” because of mindset traps, not the standards themselves. Businesses tend to avoid action or fall into one of these traps, turning VSS into a burden:
- Trap 1 – Substitution Trap: believing that “having certification = exemption” from technical barriers. Wrong — MRL, microbiological, and EUDR rules are hard barriers. VSS merely helps structure your processes to overcome them consistently.
- Trap 2 – Overextension Trap: adopting multiple standards before having strong data–segregation foundations. The solution is to focus on one core standard aligned with your target segment; build a solid micro-lot before expanding.
To join global value chains and retain value, businesses must turn market requirements into internal capabilities. The shortest path is to redesign the business model around ESG, then use VSS to standardize and demonstrate performance.
From A Ngum (Gia Lai) to Nguyễn An Sơn (Đắk Lắk), both cases prove that ESG is a set of technical and managerial decisions that yield stable productivity, transparent data, lower risk costs — and thereby reduce expenses and increase success probability when pursuing VSS certification.
Note: At the time of writing, the EUDR has been announced by the European Commission to be postponed for another year due to technical reasons, pending approval by the Parliament and member states — but the direction toward geolocation, traceability, and supply segregation remains unchanged.
#GreenExportMindset #GreenExport #ESG #GEVA #KisStartup
© Copyright KisStartup. Content developed under the GEVA Project – Green Export Acceleration through Voluntary Sustainability Standards (VSS). Any reproduction, citation, or reuse must credit KisStartup/GEVA.
References
- EU – MRL (0.01 mg/kg default when no specific MRL): European Commission, EU legislation on MRLs (Food Safety)
- EU – EUDR (traceability, geolocation, compliant/non-compliant segregation): European Commission Green Forum, Traceability and geolocation of commodities subject to EUDR
- EUDR – One-year postponement update: Reuters; Financial Times
- VSS – Market trends and data: ITC, State of Sustainable Markets 2023
- Certification cost structure (context-dependent): Rainforest Alliance, How Much Does Certification Cost?; Fee Catalogue for Certification Bodies
- Field example – Gia Lai (A Ngum, organic–microbial farming): Dân Việt; Báo Gia Lai
- Field example – Đắk Lắk (Nguyễn An Sơn, multi-stem, drip irrigation, OCOP 3-star): Dân Việt; Báo Đắk Lắk